Mpls Crime Watch - Keeping Data On Track
Table of Contents
- What's the Deal with MPLS and Our Digital Paths?
- How Does MPLS Keep a Watch on Data Flow?
- The Core Idea Behind MPLS: Labels and Speedy Routes
- Why Do We Need This 'Crime Watch' for Data?
- MPLS in Action: Routing Data with a Keen Eye
- Is MPLS Like a Digital Patrol for Network Traffic?
- Beyond the Basics: What Else Does MPLS Do?
What's the Deal with MPLS and Our Digital Paths?
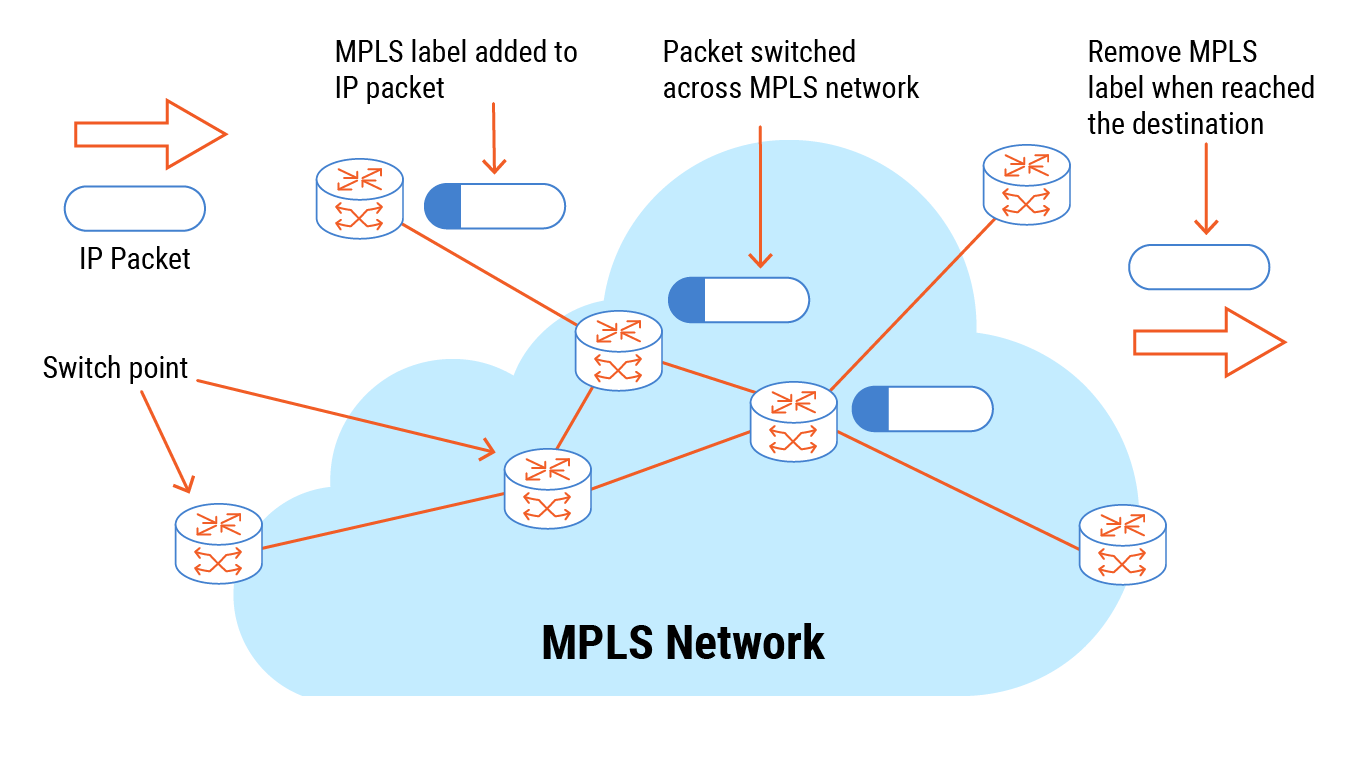
Multiprotocol label switching, which people often just call MPLS, is a way information finds its path across big communication setups. It guides data pieces from one spot to another using special markers, or 'labels,' instead of the usual internet addresses, you know? Think of it like a very clever postal service that doesn't just read the street address every single time, but instead puts a quick, easy-to-spot sticker on the package to tell it exactly which express lane to take.
This MPLS, it's actually a system for making quick, specific routes for data to travel through various networks, like your own private highway for information. When data packets usually move through a network, each device along the way has to look up the full destination address to figure out where to send the packet next. This can take a little bit of time, especially in very busy networks. MPLS changes that by assigning a short label to each packet when it first enters the network. This label tells the network devices exactly where the packet should go next, so they don't have to do a full address lookup every single time, which is pretty neat.
So, instead of a lengthy address search at every stop, these labels mean that once a packet has a label, subsequent devices just need to read that simple label to forward it along its pre-determined path. This makes the whole process much faster and smoother, kind of like having a pre-planned itinerary for your data's trip. It helps to keep things moving along without a lot of unnecessary stops or delays, which is a big deal for how quickly we get our information.
How Does MPLS Keep a Watch on Data Flow?
MPLS was made to help little bundles of data get where they need to go in a speedy and less wasteful way, so they arrive without much fuss. This focus on getting things to their destination quickly and with minimal effort is where the idea of a "watch" on data flow comes in. It's about ensuring that the digital traffic is moving as it should, without any unexpected detours or slowdowns that could affect its journey.
You can learn a bit more about what MPLS means in the world of networks and how it operates, but the core idea is simple: it's about efficiency. When you have a system that's constantly checking these labels and sending data along its best path, it's like having a very attentive observer making sure everything is running perfectly. This kind of careful observation helps to keep the entire network moving at its best pace, making sure that every bit of information reaches its home without delay.
It's quite different from other common ways networks send information around, which often rely on more complex, step-by-step address lookups. With MPLS, the "watch" is built into the system itself, making sure that once a path is set, data sticks to it. This helps to prevent congestion and ensures that critical information gets priority, which is actually a very important aspect of how our online world stays responsive and reliable, especially when you're dealing with live video calls or online gaming, for instance.
The Core Idea Behind MPLS: Labels and Speedy Routes
MPLS, as a matter of fact, is a network method that sends data along the quickest route. It does this by using those 'labels' we talked about, rather than the regular network addresses, to get things moving. Imagine you're sending a package, and instead of writing the full address on it, you put a special color-coded sticker that tells the post office exactly which conveyor belt and sorting machine it should go through at each step. This makes the process much quicker because no one has to stop and read a long address every time.
When MPLS is directing traffic, special parts of the network, called Label Switch Routers, take incoming internet packets and add an MPLS tag right between different network layers. This means they wrap up the connection, kind of, so that the label is easily visible and usable by the next device in line. It's like putting a clear instruction sheet on the outside of a box, rather than having to open the box to see what's inside and where it's going, which saves a lot of time and effort.
This process of adding a label and creating a specific path means that the network doesn't have to constantly recalculate the best way to send each piece of data. Once a path is set up for a certain type of traffic, all subsequent packets for that traffic simply follow the labels. This leads to a smoother flow of information, which is pretty essential for things like streaming video or making voice calls over the internet, where even tiny delays can cause problems, you know?
Why Do We Need This 'Crime Watch' for Data?
MPLS helps reduce the extra work that central network devices have to do when sending things along. This helps them get their tasks done with less effort, which is really good. In a way, this is where the idea of a 'crime watch' for data becomes relevant – not for actual crimes, but for preventing the 'crimes' of inefficiency, slowdowns, and wasted effort in the network. When routers have less work to do, they can handle more traffic and keep things moving without getting bogged down.
It's worth noting that MPLS was built to work with a lot of different kinds of network setups, so it's quite adaptable. This adaptability means it can be applied in various situations to keep data flowing optimally. If a network is like a busy city, MPLS acts like a traffic controller that sets up express lanes and clear signage, making sure that cars (data packets) don't get stuck in traffic jams or take unnecessary detours. This kind of proactive management is what helps keep the network 'safe' from performance issues.
The reduction in forwarding overhead means that network resources are used more effectively. Instead of spending time looking up addresses, devices spend more time actually moving data. This makes the entire system more responsive and reliable. So, in essence, this 'crime watch' is about maintaining a highly efficient and orderly environment for data, ensuring that every piece of information gets to its destination without any 'mishaps' or delays caused by a less organized system. It's about proactive care, basically.
MPLS in Action: Routing Data with a Keen Eye
MPLS is a way of directing traffic that people use in big, spread-out networks, like those covering large areas. These are often called Wide Area Networks, or WANs. In such vast networks, getting data from one side to the other quickly and reliably can be a real challenge. MPLS steps in to provide a more streamlined approach, ensuring that data doesn't get lost or delayed as it crosses long distances. It's almost like having a very precise map and a dedicated guide for every parcel of data.
MPLS uses those labels instead of regular network addresses to find the very best path for information to travel. This is where the 'keen eye' comes into play. The system isn't just blindly sending data; it's using these labels to direct traffic along paths that have been chosen for their speed and reliability. This means that even if a network has many possible routes, MPLS will guide the data along the most efficient one, avoiding congested areas or slower links, which is quite helpful.
This method of label-based switching helps to create a more predictable flow of data. When you know exactly which path your data will take, it's easier to manage network resources and ensure consistent performance. It's a bit like a train system where each train has a specific route number, and all the switches are set in advance to guide it without needing a conductor to manually check the destination at every single junction. This level of foresight helps to keep everything moving smoothly and on schedule.
Is MPLS Like a Digital Patrol for Network Traffic?
MPLS is a way of doing things that was put together to make data move faster and with less waste across big networks, or at the points where networks connect to other places, you know? These 'edge locations' are where a lot of data enters or leaves a network, and keeping things running smoothly there is very important. Think of it like a digital patrol that's constantly ensuring traffic flows freely, preventing bottlenecks and keeping an eye on the overall health of the digital roads.
When those Label Switch Routers get an internet packet, they add an MPLS marker right between the third and second layers of the network setup. This means they basically wrap up the connection, making it ready for its labeled journey. This wrapping process is a key part of how MPLS creates its efficient paths. It's like putting a special tag on a package that not only identifies its destination but also tells every handler exactly how to process it quickly, without needing to open it up and inspect its contents every time.

¿Qué es la red MPLS y cómo funciona?: ¿Qué es la red MPLS y cómo funciona?

MPLS: What is MPLS ? How to implement MPLS?
What Is MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)? | IPTP Networks